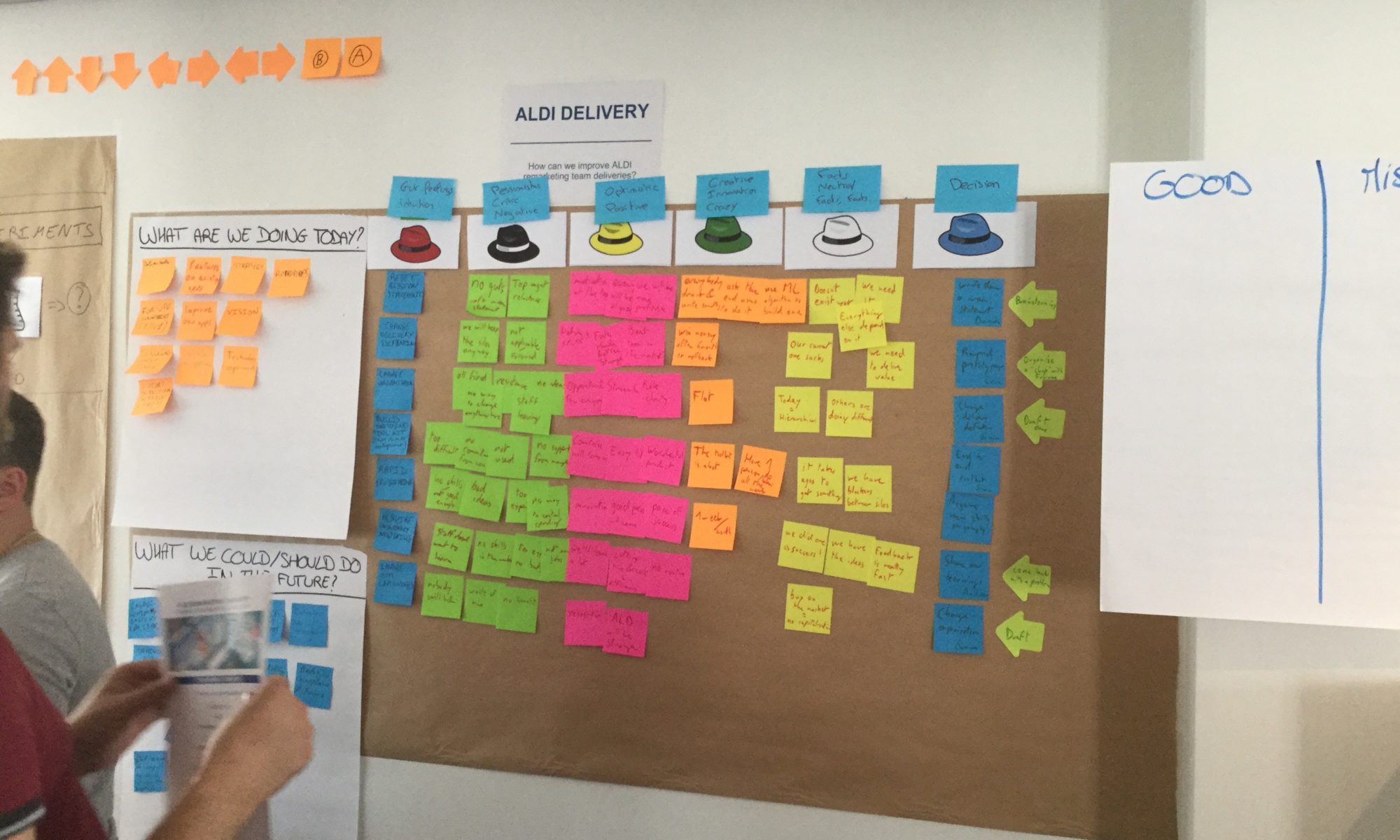
The founding objective of visual management is “observe AND see”, in the field. The land is understood as the place where value is created.
Visual management is the foundation of the entire Lean system and has also become that of the Agile system.

Principles from Lean
- A tool that at Toyota is used everywhere, by everyone and at all times
- Visual management plays an important role in the development of strategic management through the transparent display of the results of the team or department. This allows at a glance to compare the expected objectives and the achievements.
- An act of commitment from the team, and the management who will be able to face this visual Observe deviations, abnormal events, and therefore SEE the problems, visualize the degree of progress We will only be able to solve the problems that we identified.
Visual Management was widely used in factories and little in offices. Agility, and in particular the SCRUM artefacts, simplifying the visual to only 3 columns has given new impetus to this visual display.
The list of visual management tools is only limited to the imagination of the employees involved.
What is visual management?
Visual management is everywhere in the company because it allows the information to be shared to be gathered in one place
Visual management thus makes it possible to:
- Remind the people involved of the sequence of tasks to be performed (avoid errors)
- Strengthen the detection of anomalies (5S, process),
- Encourage support people to come and see and act in the field,
- Simplify exchanges on problem solving or improvement of processes and workstations,
- Facilitate involvement towards the achievement of objectives,
- Promote the improvement actions implemented,
- Create a climate based on transparency and constructive exchange.
Some ideas for visual display specific to Lean
• A hydraulic pressure gauge whose area of normal operation on this machine is marked in red paint. Too low or too high a pressure will be instantly visible to the operator or anyone passing by.
• Paint marking of tool shapes on the workstation storage board. A missing tool can be found and replaced (or substituted) before its absence becomes a problem.
• Ground markings of movement, storage and waste areas.
• .A simple and up-to-date graph of the daily goal to be achieved and the result obtained and an overall graph for the entity or company with the same type of data.
Examples of generic display in visual management
• Common objective and common strategic information
• Diagrams, graphics
• Kanban cards
• Color lines and color coding
• Signs, labels
• Control or progress panels
• Zone information signs
• Dials, gauges
• Check-lists
Examples of displays specific to Agile visual management
• A list of User stories actions, listed to Do
• Actions in progress, retorted in progress
• Actions under test,
• Finished actions
Who are the beneficiaries of visual management?
All employees are beneficiaries. The goal is to share the same information to facilitate understanding of everyone’s tasks and to simplify problem solving.
It is not a management tool in the traditional sense, but an individual and collective performance tool to be developed by everyone to simplify everyone’s life and focus on creating value.
Author: Dominique popiolek-Ollé, Transmutation leader, Agile Executive Coach, Founder of In Imago, management consulting and disruptive transformation.